Digestive Issues in Horses
Assorted Digestive Issues in Horses
This page provide easier access to at a variety of digestive issues in horses. Follow the Linked panels below for Topics desired. Specific information will be provided for each topic plus tips on how Nzymes® Digestive Products can support healthier digestion.
Digestive Issues in Horses of All Ages
Add the Power of Nzymes® Digestive Products for Your Horse
Nzymes® Bac-Pak Plus is a powerful Probiotic & Digestive Enzyme blend. It is the perfect solution for digestive issues in horses. Only small amounts are required every day for a horse’s healthier digestion. We can use less because of the special “Micro-Encapsulation Process”. To begin with, it provides protection against external heat sources that can damage most probiotics and enzymes even before they are used. Secondly, it slows damage from stomach acid and allows the majority of viable bacteria to reach the GI tract. Bac-Pak Plus promotes proper digestion and the natural assimilation of foods.
Bac-Pak Plus was created as digestive supplemental for animals of all ages. It is especially effective to help optimize a horse’s digestive tract and immune system. For pennies a day, your horse can benefit from the added support of this highly concentrated blend of digestive enzymes and direct-fed microbials (probiotics).
How Probiotics & Digestive Enzymes Work in the System
Probiotics
How Do Probiotics Work?
To begin, Probiotics work by attaching themselves to the intestinal wall. These friendly bacteria keep pathogenic bacteria from gaining a foothold. In addition, they produce lactic acid and hydrogen peroxide, (which kill most disease-causing bacteria). For instance. some yogurt and other fermented food have these cultures. However, they may not be strong enough for the problems being caused in today’s environment. This is why daily supplementation with Probiotics is so important. Lastly, it costs only a few pennies a day to supplement yourself and your pets
What Are The Benefits?
In large enough numbers, these friendly bacteria keep disease-causing bacteria from overpopulating the intestine. Also, they improve digestion, manufacture B vitamins, and boost immune system activity. Because they boost immunity, they positively influence the overall health of the individual.
Understanding Probiotics
Probiotics help supplement the production of Lactic Acid-producing bacteria. In the digestive tract, this helps in balancing the pH and the colonization of beneficial bacteria. This creates a hostile environment for undesirable bacteria to take hold. Also, they enhance the growth of several digestive enzymes found in various stages in the digestive system. The synergistic effect aids in maintaining more normal intestinal functions.
Probiotic Cultures
Lactobacillus Acidophilus – Micro-encapsulated species specific, to stimulate natural lactic acid production. This creates a sudden downshift in the pH in the small intestine. Increasing levels of lactic acid allow for greater fluid and nutrient transfer across the intestinal wall. Lactobacillus acidophilus is the most commonly used probiotic, or “friendly” bacteria. Such healthy bacteria inhabit the intestines and vagina and protect against the introduction and proliferation of “bad” organisms that can cause disease.
Lactase
The breakdown of food by L. acidophilus leads to the production of lactic acid, hydrogen peroxide, and other by-products that make the environment hostile for undesired organisms. L. acidophilus also produces lactase, the enzyme that breaks down milk sugar (lactose) into simple sugars. People who are lactose intolerant do not produce this enzyme. For this reason, L. acidophilus supplements may be beneficial.
Bifidobacterium Thermophilum – Micro encapsulated species-specific, designed to be viable (live) until It reaches the small intestine, aids in stimulating the lactic acid production. A very beneficial colonizer in the intestinal tract that replaces the space vacated by the undesirable bacteria after a downshift In the pH. This particular strain is very quick to colonize (multiply) in the intestinal tract.
Bifidobacterium longum – Micro-encapsulated for storage and viability until it reaches the lower gut (small intestine). This provides a very quick response time at colonizing (attaching to the lining of the intestinal tract) therefore leaving less space for undesirable bacteria to attach. It also helps to maintain a higher percentage of fluid and nutrient assimilation through the intestinal wall.
Enterococcus faeclum – Micro-encapsulated, this durable strain of bacteria is a great stimulate of lactic acid production in the intestinal tract of the individual. This particular strain is very beneficial in the synthesizing of B vitamins.
Bacillus Subtilis – A very durable strain of bacteria. It enhances lactic acid production. This particular strain demonstrates properties that have been shown to reduce nitrates. It also stimulates the production of additional enzymes like amylase, protease, and lipase.
Digestive Enzymes
How Do Digestive Enzymes Work?
Specific digestive enzymes break down the major substrates of nutrients that are being consumed. Thus enhancing the overall nutrient assimilation of the food that is being consumed. This relates to more bio-available nutrients being used for the health of the Individual and less being passed away in the stools.
Digestive Enzyme Species
Amylase – increases the utilization of starches that are being consumed. It does this by reducing the molecules to smaller molecular weights. Thus, more can be more readily absorbed into the blood system.
Protease – or proteolytic enzymes enhances the utilization of the proteins that are being consumed. It does this by reducing them to usable peptides and amino acids which make this substance more bio-available to the individual. Protease helps to clean up your body by removing the unwanted protein from your circulatory system and bloodstream and helps restore your energy and balance.
Hemi-cellulase – readily digestible cellulose is held in bundles by Hemi-cellulose fractions. Hemi-cellulase specifically aims at and breakdown these Hemi-cellulose fractions opening up the cellulose to make it more available for digestion.
Phytase – hydrolyzes phytic acid which is widespread. This is the principal form of phosphorus in many seeds. Phytic acid contents are about 60-80% of the total phosphorus in seeds. Lastly, Phytic acid binds minerals such as iron, zinc, calcium, and magnesium, therefore it reduces their bio-availability.
Cellulase – enhances the utilization of the fibrous portions of the food being consumed.
Lipase – helps to supplement the inherent enzyme system in the break down of fats and lipids. Also increases the bio-availability of fat-soluble vitamins.
Pectinase – reduces the structure size of the plant pectin into galacturonic acid. It does this to maintain water balance to avoid excessive fluid passage, which is essential for cell growth and development.
Beta-glucanase – specific enzyme to hydrolyze and enhance the bio-availability of specific types of starch molecules.
Fiber
Yucca Schidigera Powder
Yucca Schidigera – is a natural plant fiber that has ammonia binding capabilities. This helps stimulate blood flow by reducing blood cholesterol and abnormal blood triglycerides. It also helps to reduce the inflammation in joints, which include chronic arthritis. It decreases the amount of toxins available for absorption from the digestive system. The body’s kidneys, liver, lymph, and blood system are thus less taxed to remove poisons from the body. This lowers the build-up of toxins in the joints which can relate to diseases like arthritis.
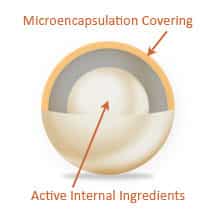 Micro-Encapsulation
Micro-Encapsulation
Protected By Micro-Encapsulation
The special Micro-Encapsulation process protects against damage from external heat and stomach acid. The result ensures that 95% of the viable bacteria penetrate to the GI tract.




